About Us
One place where the world's nations can
gather together, discuss common problems
and find shared solutions.
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945. Currently made up of 193 Member States, the UN and its work are guided by the purposes and principles contained in its founding Charter.
The UN has evolved over the years to keep pace with a rapidly changing world.
But one thing has stayed the same: it remains the one place on Earth where all the world’s nations can gather together, discuss common problems, and find shared solutions that benefit all of humanity.
The World We Want - 75 photos curated from more than 50,000 images from over 130 countries in response to the Secretary-General’s call to hear directly from the peoples of the world about their priorities for the future.
Member
States
The UN’s Membership has grown from the original 51 Member States in 1945 to the current 193 Member States.
All UN Member States are members of the General Assembly. States are admitted to membership by a decision of the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council.
Secretary-General
In the end, it comes down to values [...] We want the world our children inherit to be defined by the values enshrined in the UN Charter: peace, justice, respect, human rights, tolerance and solidarity.
António Guterres
United Nations Secretary-General
The Secretary-General is Chief Administrative Officer of the UN – and is also a symbol of the Organization's ideals and an advocate for all the world's peoples, especially the poor and vulnerable.
The Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a 5-year, renewable term.
The current Secretary-General, and the 9th occupant of the post, is António Guterres of Portugal, who took office on 1 January 2017.
On the 18th of June, 2021, Guterres was re-appointed to a second term, pledging as his priority to continue helping the world chart a course out of the COVID-19 pandemic.
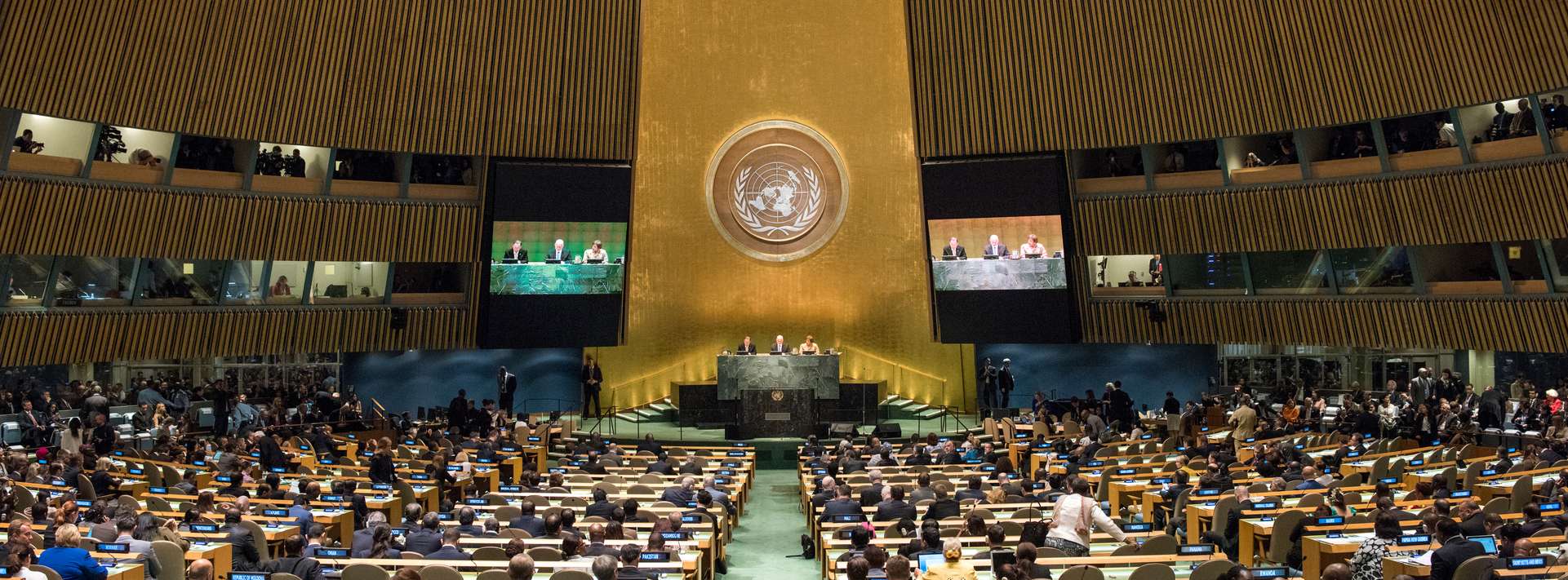
Main Bodies

©UN Photo/Cia Pak
The main bodies of the UN are the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the UN Secretariat.
All were established in 1945 when the UN was founded.
Secretariat

©UN Photo/Manuel Elías
The Secretariat carries out the day-to-day work of the UN as mandated by the General Assembly and the Organization's other main bodies.
The Secretary-General is the head of the Secretariat, which has tens of thousands of international UN staff members working at duty stations all over the world.
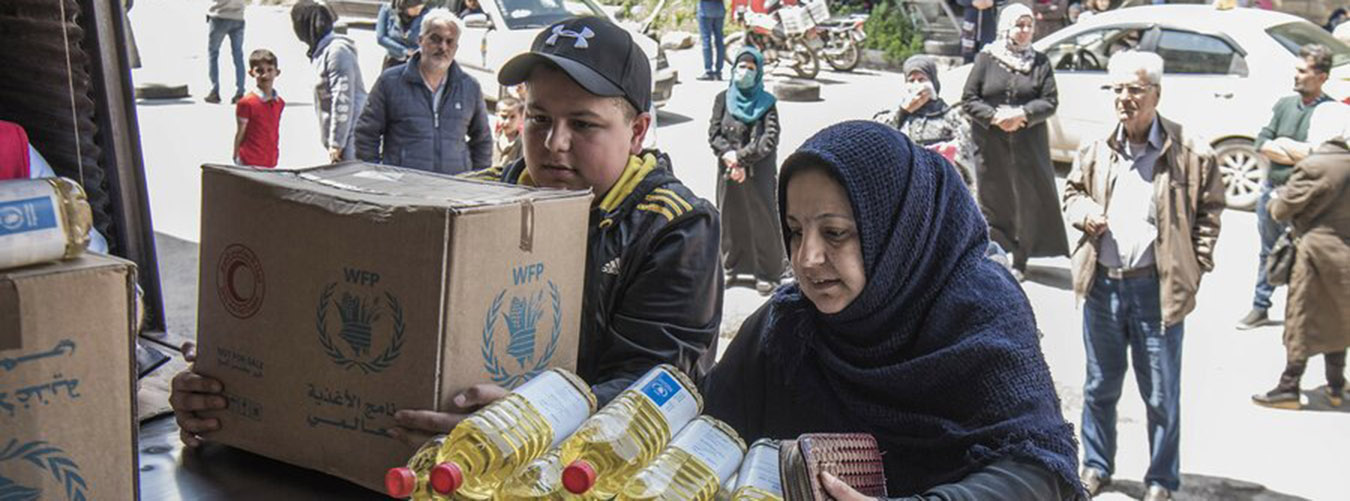
UN System

©WFP/Ali Habib
The United Nations is part of the UN system, which, in addition to the UN itself, comprises many programmes, funds and specialized agencies, each of which have their own area of work, leadership and budget.
The UN coordinates its work with these separate UN system entities, all of which cooperate with the Organization to help it achieve its goals.
UN Emblem and Flag
The UN’s symbol — who designed it? what does it mean?
UN History
- Overview
- Milestones in UN History
Timeline from 1941 to the present
- The San Francisco Conference
51 countries sign the UN Charter creating a new organization
- Preparatory Years: UN Charter History
Events which led to the UN’s creation
- Predecessor: The League of Nations
The League of Nations and the first international organizations
UN Charter

The Charter that our founding 51 Member States signed 75 years ago to create the UN
Full text
Individual chapters and more
UDHR

Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) — widely recognized as having inspired the adoption of more than 70 human rights treaties
Full text
History of, drafters, and more
The ICJ Statute

Statute of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) — How is the Court constituted? How does it function?
Full text
The ICJ is the main judicial organ of the UN

Nobel Peace Prize
The UN, UN system entities, and staff have been awarded the Nobel Peace Prize more than ten times.