NATO is an intergovernmental military alliance formed for collective defense among North American and European countries.
Several UN-affiliated bodies and organizations work in humanitarian aid, such as the Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), World Food Programme (WFP), United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), and the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC). These entities provide emergency assistance, aid, and support to populations affected by conflicts, disasters, and other crises worldwide.
The ILO establishes international labor standards, promotes decent work for all, and addresses labor-related issues, including labor rights, employment opportunities, and social protection.
UNESCO works to promote peace and security through international collaboration in education, sciences, culture, communication, and information.
UNDP focuses on poverty reduction, democratic governance, crisis prevention and recovery, environment and energy for sustainable development, and more.
UNICEF works with governments, partners and other UN agencies to support countries around the world to ensure that the SDGs deliver results for every child - now and for generations to come.
Poverty eradication and respect for human rights, central pillars of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), are at the core of UNRWA’s human development, humanitarian and protection work. The SDGs central to its work are: SDG 1: No Poverty; SDG 2: Zero Hunger; SDG 3 Good Health and Well-Being; SDG 4: Quality Education; SDG 5: Gender Equality; SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation; SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth; SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities; SDG17: Partnerships.
The Department of Economic and Social Affairs (part of the UN Secretariat) engages stakeholders around the world in the implementation, evaluation and monitoring process of the SDGs.
UN Regional Economic Commissions play a critical role in supporting countries in their efforts to implement the 2030 Agenda by providing technical capacity and analytical work and policy advisory services, and serving as platforms for dialogue. The UN's Regional Economic Commissions are part of the UN Secretariat.
The Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) has emphasized the importance of planning as a key tool of policymaking and public management. Countries in the Latin America and the Caribbean region have made significant commitments and taken steps to integrate the Sustainable Development Goals into their national or subnational planning schemes.
ECA supported Member States in achieving regional cooperation and integration, and contributed to the establishment of the African Continental Free Trade Area by 44 African countries, which will create a single continental market for goods and services that can deliver economies of scale, improved competitiveness, foreign direct investment and poverty reduction (SDG Goal 1).
UNICEF focuses on providing humanitarian and developmental assistance to children and mothers in developing countries, ensuring they have access to healthcare, clean water, education, and protection from violence and exploitation.
The WHO is responsible for international public health and deals with health-related issues, including disease outbreaks, health emergencies, vaccinations, and global health policy.
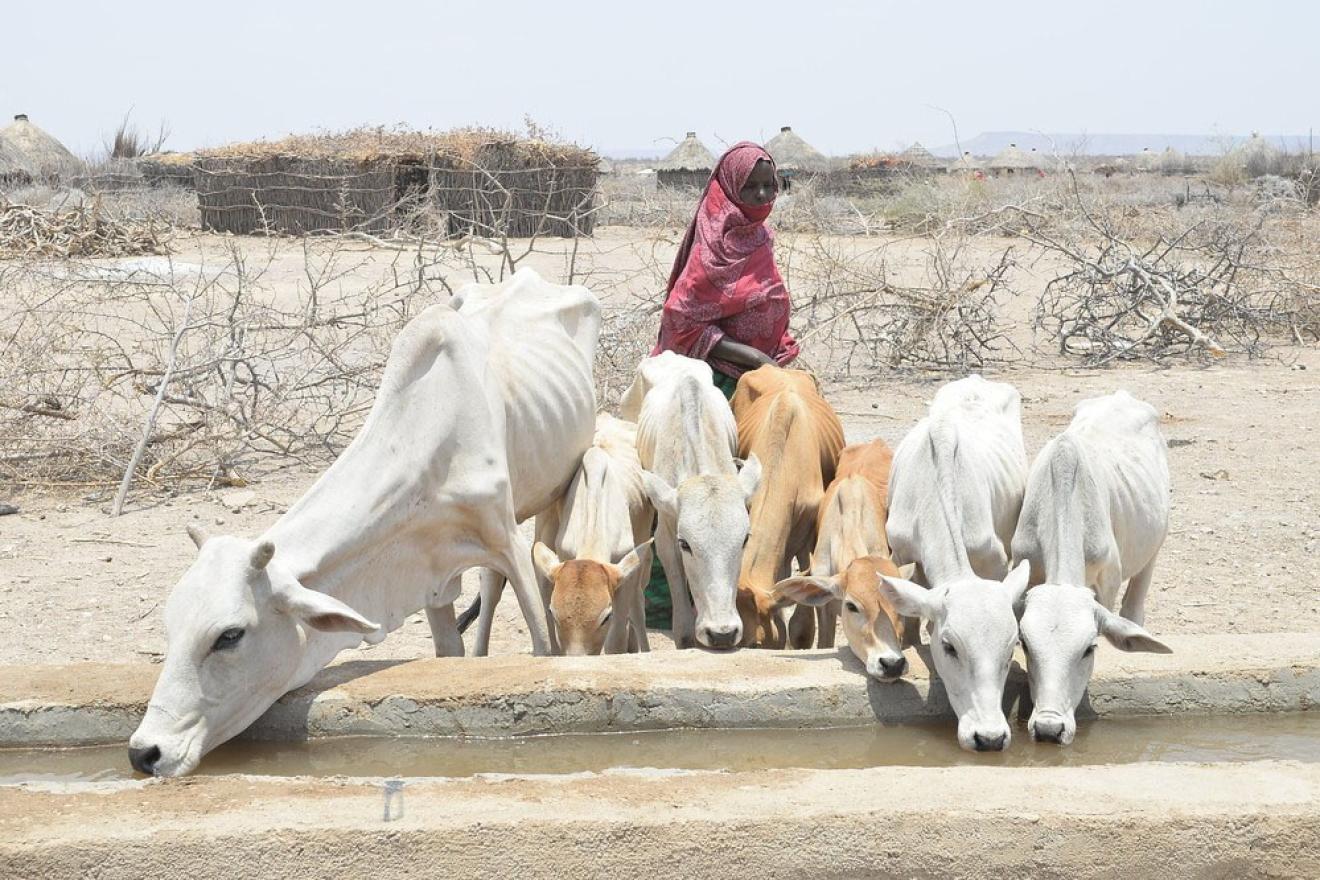
FAO leads international efforts to combat hunger, achieve food security, and promote sustainable agriculture practices worldwide.
UNHCR protects and supports refugees globally, ensuring their rights are upheld and assisting in finding durable solutions for their situations.
UN Women works for gender equality and the empowerment of women globally, advocating for women's rights, participation in decision-making, and ending gender-based violence.
Goal 2 of the Sustainable Development Goals – Zero Hunger – pledging to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture, is the priority of the World Food Programme.
Contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals by sustainably building a world without hunger, malnutrition and poverty is the goal of FAO.
Given its goal of transforming rural areas and its unmatched experience in investing in smallholder farmers, IFAD plays a central role in achieving SDGs 1 (no poverty) and 2 (zero hunger).
IMO’s Technical Cooperation Committee has formally approved linkages between the Organization’s technical assistance work and the SDGs. While the Oceans goal, SDG 14, is central to IMO, aspects of the Organization's work can be linked to all individual SDGs.
Information and communication technologies (ICTs) can help accelerate progress towards every single one of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). ITU contributes to SDG 9 in particular—helping to build resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation (specifically SDG Target 9.c).
UNESCO contributes to the implementation of the SDGs through its work on Education, Natural Sciences, Social and Human Sciences, Culture, Communication and information. Additionally, the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO holds a universal mandate and global convening power for ocean science and capacity development in support of the 2030 Agenda and its sustainable goals.
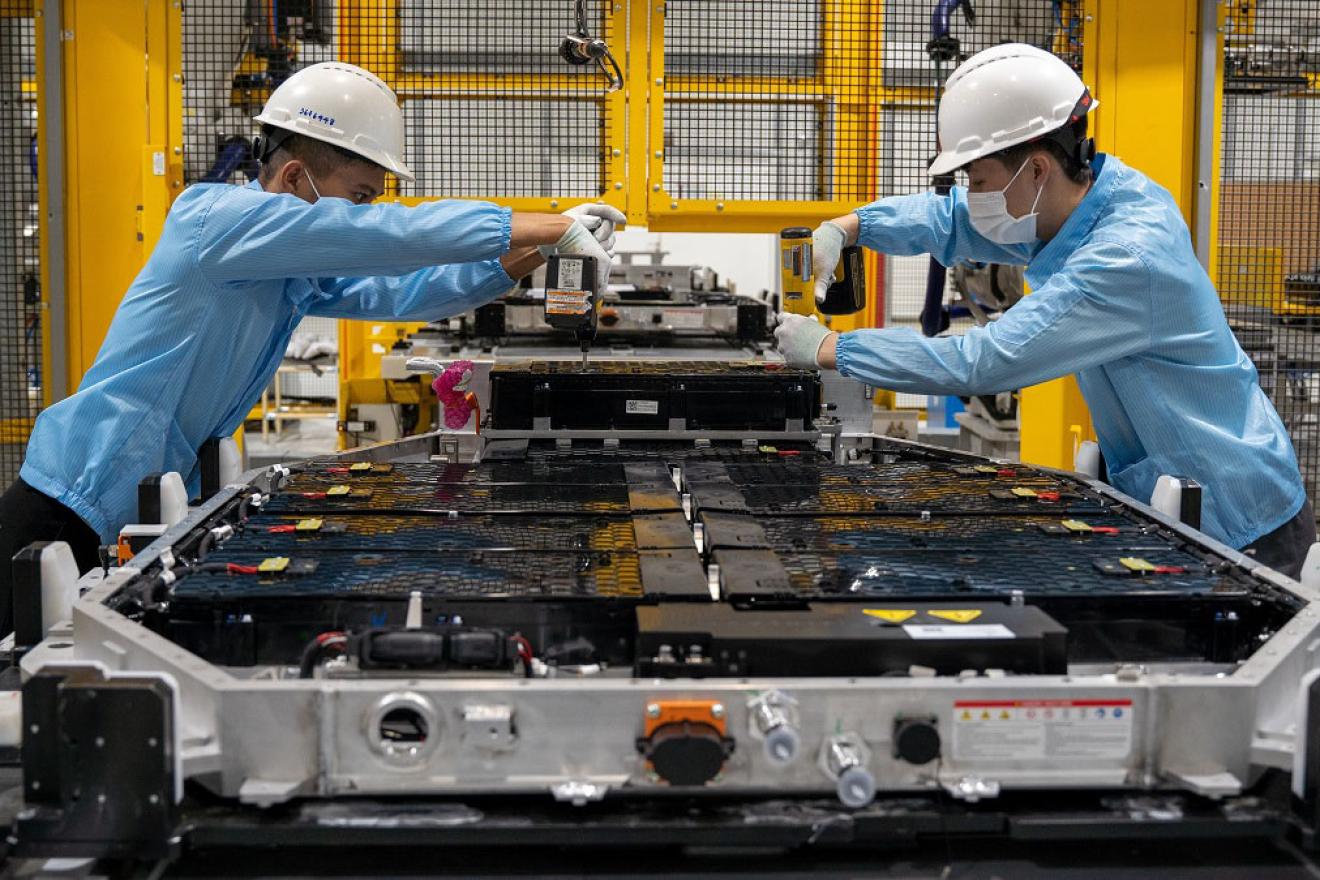
UNIDO supports all 17 SDGs, but puts a strong emphasis on SDG9, which focuses on building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation.